Before discussing on components of biomass, we should know about biomass.
Table of Contents
Biomass
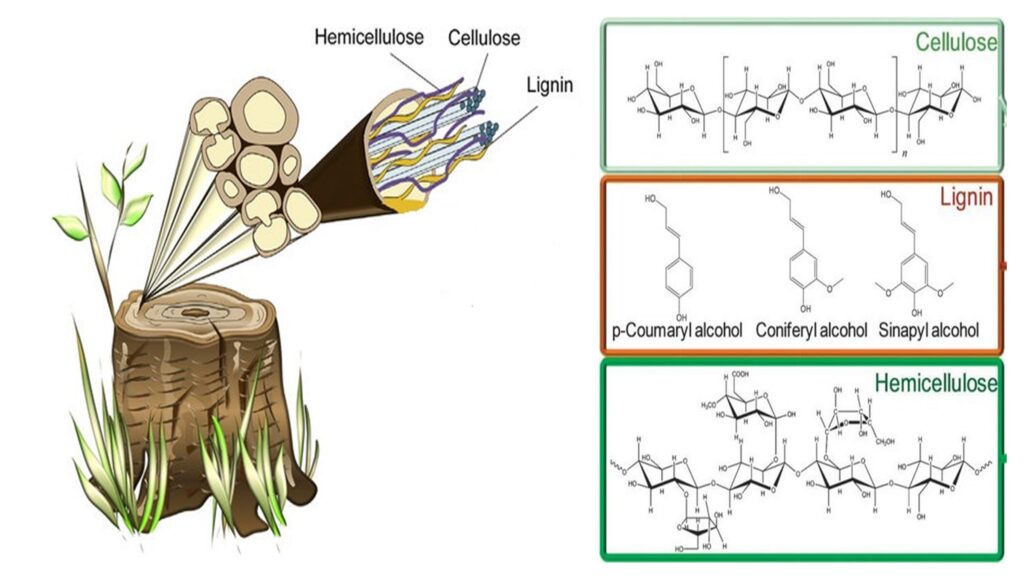
Biomass is the total amount of carbon stored in a given area. In terms of biomass, we are talking about the total mass of carbon stored in a particular area. A forest is a good example of a place where biomass is high. Soil is another great example of biomass. When we talk about biomass, we are referring to the total amount of carbon contained in a specific area. Five primary components of biomass are mainly: cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, volatiles, and ash.
Components of biomass
Five primary components of biomass are mainly: cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, volatiles, and ash.
Cellulose
Cellulose is the most abundant biopolymer on earth and is present in the primary cell wall of all green plants. It is composed of long chains of glucose molecules bound together by strong hydrogen bonds. In nature, cellulose is found in the stems and roots of trees, grasses, and many other types of plants. It is a substance that is the main part of the cell walls. Since it is made by all plants, it is probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. Aside from being the primary building material for plants, cellulose has great utility in industry.
- Formula: (C6H10O5)n, where n is the degree of polymerization and represents the number of glucose groups
- It is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants.
- It is strong, crystalline, and resistant to hydrolyze.
- Cellulose is an unbranched polymer.
- It is a very complex carbohydrate and consists of 3,000 or more glucose units.
- Tasteless, odorless, and hydrophilic
- Insoluble in water
- Biodegradable
- The melting point is 260-270 0C
Alpha cellulose: It is a major component of wood and paper pulp. It may be separated from other components by soaking the pulp in a 17.5% solution of sodium hydroxide solution under the conditions of the test.
- It has the highest degree of polymerization and is the most stable.
- Undegraded
- High molecular weight cellulose
Beta-cellulose: It is the soluble fraction that is reprecipitated on acidification of the solution.
Gamma-cellulose: It is the fraction remaining in the solution. Gamma-cellulose consists mainly of hemicellulose. The quantity of γ-cellulose tells the amount of hemicellulose in biomass.
Hemicellulose
Hemicellulose is a type of polysaccharide that is often referred to as “the glue” of the plant cell wall. It consists of long chains of xylose and arabinose molecules linked together by weak hydrogen bonds. Hemicelluloses are found in the middle lamella between the primary cell wall and the secondary cell wall. It is one of the number of heteropolymers (matrix polysaccharides) present in the cellulose cell wall of all terrestrial plants.
- It is strengthening the cell wall of plants by interacting with cellulose.
- It has an amorphous structure with little strength and can be easily hydrolyzed.
- It consists of shorter chains – 500–3,000 sugar units.
- It is an unbranched polymer.
- Gamma-cellulose consists mainly of hemicellulose
Holocellulose
It is the total carbohydrate fraction (cellulose and hemicellulose) of the raw material.
Lignin
Lignin is a complex polymer that is formed from phenolic compounds. Lignin is primarily responsible for providing rigidity to the plant cell wall. Lignin is one of the most important components of biomass. It is an important organic polymer present in abundant quantity in cell walls It has many biological functions such as water transport, mechanical support, and resistance to various stresses.
-
Natural phenolic polymers
-
High molecular weight
-
Complexity in composition and structure
-
Reduction in the accumulation of lignin in plants may increase the production of biofuels.
-
Most important is the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity and do not rot easily.
Types of lignin: The most important types of lignin are as given below:
- Milled Wood Lignin:
- Soda Lignin:
- Steam Explosion Lignin:
- Dilute Acid Lignin:
- Hydrolyzed Lignin:
- Organosolv Lignin:
- Kraft Lignin: This type of lignin is the main by-product of the Kraft pulping process. Kraft lignin is only soluble in the alkaline solution above pH 10. It is used to burn for the generation of electricity in paper mills due to its low reactivity.
- Lignosulfonates: This type of lignin is the important by-product of the sulfite process, generally used as additives, dispersant agents, binder, complexing and emulsifying agents.
- Acid Soluble Lignin: It is the lignin fraction that is soluble in 72% sulphuric acid.
- Klason Lignin: It is the amount of insoluble residue material after removing the ash by concentrated acid hydrolysis (72% H2SO4) of the plant tissues. Klason Lignin constitutes the major mass proportion of the lignin content for most biomass samples, with the remainder of lignin being classified as acid-soluble lignin.
Total Lignin = Klason Lignin + Acid Soluble Lignin
Klason Lignin = Acid Insoluble Residue – Acid Insoluble Ash
Acid Insoluble Residue: It is the amount of a sample that is not hydrolyzed by 72% sulphuric acid.
Acid Insoluble Residue = Klason Lignin + Acid Insoluble Ash
Acid Insoluble Ash: It is the amount of sample that is not hydrolyzed by 72% sulphuric acid and is not subsequently volatilized upon the incineration of this acid-insoluble residue.
If you are interested to read more about components of biomass, comment below.
Read more interesting articles:
components of biomass components of biomass components of biomass components of biomass


1 thought on “What are the 3 main components of biomass?”