People always get confused when they search for deep learning, people can not differentiate between machine learning and deep learning. DL is a subset of machine learning and machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence. We have discussed machine learning and artificial intelligence in previous articles. This article will be covered deep learning and its history. The article also explained how DL works and provide insights about its applications.
Table of Contents
What is the Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that involves training neural networks, specifically deep neural networks (DNNs). DNNs are artificial neural networks designed to work in tandem with human intelligence. These networks have been applied to many different fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, and robotics. DL is a type of supervised machine learning that involves giving a computer a training set of examples, each of which consists of an input and an output from the function being learned.
Simply,
“Deep Learning, a more advanced subset of machine learning, processes data using multiple layers of algorithms to create abstractions or to mimic the thinking process.”
History of the Deep Learning?
Deep learning and neural networks have their roots in the 1950s when British mathematician and computer scientist Alan Turing prophesied a supercomputer with human-like intelligence. We must begin our brief history of deep learning with those neural networks.
-
The perceptron is a method for pattern recognition developed by Frank Rosenblatt in 1958, that relies on a two-layer artificial neural network with just addition and subtraction.
-
Kunihiko Fukushima suggested a multilevel artificial neural network in 1980 to solve difficulties with handwriting identification and other types of pattern recognition.
-
A paper published by Geoffrey Hinton and Ruslan Salakhutdinov in 2000, demonstrated how a multi-layered neural network could be pre-trained one layer at a time, and the term “deep learning” started to acquire prominence.
-
On some tasks, artificial pattern-recognition systems perform at a human level in 2012.
-
Google purchases a British AI business in 2014, whereas in 2015 Facebook uses deep face, a deep learning technology.
-
In 2016, at a highly publicized competition in Seoul, Google DeepMind’s algorithm AlphaGo defeated professional go player Lee Sedol after mastering the complicated board game Go.
How does Deep Learning work?
DL is a subfield of machine learning that focuses on training artificial neural networks (ANN) to perform tasks using lots of data. Similar to how the human brain is made up of neurons, neural networks are layers of nodes. Individual layer nodes are linked to neighboring layer nodes. The number of layers in the network determines how deep it is considered to be. In the human brain, a single neuron takes in hundreds of impulses from other neurons. Signals travel between nodes and assign matching weights in an artificial neural network.
There are input, hidden, and output layers in deep learning neural networks. There is only one hidden layer in a simple neural network, whereas there are multiple (deep) hidden layers in a deep learning neural network.
This is the major distinction between the two types of neural networks also shown in the below figure.
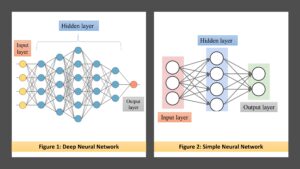
Nonlinear transformations are fed into the input layer. In the hidden layer, calculations based on input data are made. The hidden layer iteratively computes input data until it outputs accurate data. Determining the number of hidden layers and neurons for each of them in deep learning is one of the challenges. Hidden layers are all the layers that exist between input and output. Typically, each layer is a straightforward algorithm with a single type of activation function. Traditional neural networks have only 2-3 hidden layers, however, DL can have up to 150.

What are the Deep Learning algorithms?
Without human supervision, the DL algorithm can learn and be applied to both structured and unstructured data. Multiple layers of neural networks are dynamically configured to conduct DL algorithms. They are nothing more than a group of pre-trained decision-making networks that have a specific purpose. The most widely used deep learning algorithms are used for different purposes in different sectors. The top 10 DL algorithms are listed below:
-
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
-
Long Short-Term Memory Networks (LSTMs)
-
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
-
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
-
Radial Basis Function Networks (RBFNs)
-
Multilayer Perceptron’s (MLPs)
-
Self-organizing Maps (SOMs)
-
Deep Belief Networks (DBNs)
-
Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs)
-
Autoencoders
What are the applications of Deep Learning?
DL is a sub-field of machine learning that focuses on training deep neural networks, i.e., multi-layered perceptrons. DL algorithms have been successfully applied to many computer vision tasks including image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation, and caption generation. The top 10 applications of DL are enlisted below:
-
Industrial automation
-
Process Optimization
-
Military and defense
-
Aerospace
-
Healthcare
-
Customer support services
-
Self-driving cars
-
Robotics
-
Text generation
-
Object detection
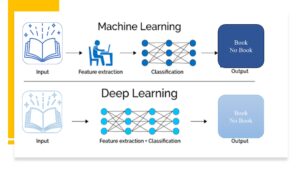
Difference between DL and ML?
Deep learning is often confused with machine learning, but they are quite different. AI can be categorized as either machine learning or deep learning. DL is focused on processing huge amounts of data and making decisions based on what it learns. DL requires lots of training data and computing power. Machine learning refers to the use of algorithms by computers to learn from data and carry out tasks automatically without explicit programming. DL employs a sophisticated set of algorithms that are designed after the human brain.
Conclusion
You would have gained the fundamentals of DL and an understanding of how deep learning works after reading this article. You studied the various DL approaches, history, and applications. Kindly post any comments you may have in the article’s comments section if you have any questions about this DL. Your questions will be answered as soon as possible. In the next articles, the DL topic will be discussed deeply.
FAQ:
Question: What is deep learning in simple words?
Answer: DL is a machine learning method that teaches computers to perform tasks that humans accomplish without thinking about it.
Question: What is deep learning used for?
Answer: DL is used to provide intelligent answers to complicated issues.
Question: Which algorithm is best for DL?
Answer: The best DL algorithm is multilayer perceptrons (MLPs).
Question: What are examples of deep learning?
Answer: Virtual assistants, Translations and image colorization etc.
Question: Why is it called deep learning?
Answer: The number of hidden layers in the neural network is typically indicated by the term “deep.”.
Question: What is the difference between deep learning and AI?
Answer: The idea of building intelligent machines is known as artificial intelligence. DL is a branch of machine learning that trains a model using enormous amounts of data and sophisticated algorithms.
Question: What are the 3 Deep Learning Layers?
Answer: The input, hidden, and output layers make up the three layers of the three-layered neural network.

