Welcome to the world of Environmental Science and Engineering! This field is dedicated to understanding and protecting our planet’s natural resources and ecosystems. Chemical Engineering plays a crucial role in this domain as it helps in developing sustainable solutions for environmental problems. Environmental Science and Engineering is a multidisciplinary field that combines scientific principles and engineering techniques to address environmental challenges and promote sustainable practices. It involves the study of the environment, its components, and the interactions between human activities and the natural world. This article provides an overview of the key concepts and objectives of Environmental Science and Engineering. In this blog post, we will introduce you to the basic concepts of Environmental Science and Engineering and explore how Chemical Engineering is used to tackle environmental issues that we face today. So, let’s dive in and explore this fascinating field!
Table of Contents
The basic concept of Environmental Science
The basic concepts of Environmental Science revolve around the understanding of the natural environment, its components, and the interactions between human activities and the environment. Here are some key concepts in Environmental Science:
Ecosystem: An ecosystem is a community of living organisms (plants, animals, and microorganisms) interacting with each other and their physical environment. It involves the study of ecological relationships, energy flow, and nutrient cycling within a particular area.
Biodiversity: Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms in an ecosystem, including the diversity of species, genetic diversity, and ecosystem diversity. It is important for the stability and resilience of ecosystems and provides numerous benefits, including ecosystem services and potential sources of medicine and food.
Pollution: Pollution refers to the introduction of harmful substances or contaminants into the environment. It can occur in various forms such as air pollution, water pollution, soil pollution, and noise pollution. Environmental Science focuses on understanding the causes, impacts, and mitigation of pollution.
Climate Change: Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperature and weather patterns on Earth. It is primarily caused by human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, leading to increased greenhouse gas emissions. Environmental Science studies climate change impacts, mitigation strategies, and adaptation measures.
Natural Resources: Natural resources are materials or substances that occur naturally in the environment and are valuable to human beings. They include air, water, soil, minerals, forests, and wildlife. Environmental Science emphasizes the sustainable management and conservation of natural resources.
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA): EIA is a process used to assess the potential environmental consequences of proposed development projects. It involves identifying and evaluating the environmental, social, and economic impacts of a project before it is implemented. EIA helps to ensure that projects are environmentally sustainable and comply with regulations.
Sustainability: Sustainability involves meeting the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It encompasses environmental, social, and economic aspects. Environmental Science promotes sustainable practices that balance human activities with the preservation and conservation of the environment.
Conservation: Conservation involves the protection, preservation, and management of natural resources and ecosystems. It aims to maintain biodiversity, prevent habitat loss, and promote sustainable use of resources. Environmental Science plays a crucial role in studying conservation strategies and implementing conservation measures.
Renewable Energy: Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and biomass, are alternatives to fossil fuels that can help mitigate climate change and reduce dependence on non-renewable resources. Environmental Science explores the potential of renewable energy technologies and their environmental benefits.
Environmental Policy: Environmental policies are laws, regulations, and guidelines implemented by governments to protect the environment, promote sustainable development, and regulate human activities. Environmental Science provides scientific insights and data to support the development and implementation of effective environmental policies.
These basic concepts form the foundation of Environmental Science and guide the study, understanding, and management of the natural environment and its resources. By applying these concepts, Environmental Science aims to address environmental challenges, promote sustainability, and create a harmonious relationship between human activities and the environment.
The basic concept of Environmental Engineering
The basic concepts of Environmental Engineering revolve around the application of scientific and engineering principles to protect and improve the quality of the environment. It involves the study and implementation of various technologies and strategies to address environmental challenges. Here are some key concepts in Environmental Engineering:
Water and Wastewater Treatment: Environmental Engineering focuses on the treatment and management of water resources, including the supply of clean drinking water and the treatment of wastewater. It involves processes such as filtration, disinfection, sedimentation, and biological treatment to remove contaminants and ensure the safety of water for human use and ecosystem health.
Air Pollution Control: Environmental Engineering addresses the control and mitigation of air pollution. This includes the study and implementation of technologies to reduce emissions from industrial processes, power plants, vehicles, and other sources. It involves the use of filtration systems, scrubbers, catalytic converters, and other methods to remove pollutants and improve air quality.
Solid Waste Management: Environmental Engineering focuses on the proper management of solid waste to minimize environmental impact. It involves strategies for waste reduction, recycling, composting, and safe disposal of waste materials. It also includes the design and operation of landfill facilities to ensure proper containment and management of solid waste.
Hazardous Waste Management: Environmental Engineering deals with the identification, handling, treatment, and disposal of hazardous waste materials. It includes the development of protocols and technologies to safely manage and dispose of hazardous substances, such as chemicals, radioactive materials, and biomedical waste, to protect human health and the environment.
These basic concepts form the foundation of Environmental Engineering and guide the application of engineering principles to address environmental challenges. By applying these concepts, Environmental Engineering aims to protect and improve the quality of the environment, promote sustainable development, and ensure the well-being of both human and ecological systems.
Difference between Environmental Science and Environmental Engineering.
Environmental Science and Environmental Engineering are two closely related fields that focus on understanding and addressing environmental issues. While they share common goals of protecting and preserving the environment, there are distinct differences between the two disciplines. Here are some key differences:
Focus and Perspective
Environmental Science: Environmental Science is a multidisciplinary field that focuses on studying the natural environment and its interactions with human activities. It encompasses the study of ecological systems, environmental processes, and the impact of human activities on the environment. Environmental scientists seek to understand the complexities of the environment and provide insights into environmental problems.
Environmental Engineering: Environmental Engineering, on the other hand, is an applied field of engineering that involves the design, implementation, and management of technologies and systems to solve environmental problems. It emphasizes the application of engineering principles, techniques, and technologies to address environmental challenges and ensure sustainable solutions.
Approach
Environmental Science: Environmental Science adopts a holistic and scientific approach to studying the environment. It involves conducting research, collecting data, and analyzing the interactions between physical, chemical, and biological components of the environment. Environmental scientists study the complex systems and processes to gain a deeper understanding of environmental issues.
Environmental Engineering: Environmental Engineering takes an engineering approach to address environmental challenges. It involves the application of scientific and engineering principles to develop practical solutions. Environmental engineers design and implement technologies, systems, and processes to mitigate environmental pollution, manage resources, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Scope of Work
Environmental Science: Environmental scientists conduct research, collect data, and analyze environmental samples to study various aspects of the environment. They investigate pollution sources, assess environmental impacts, and contribute to the development of environmental policies and regulations. They may work in research institutions, government agencies, consulting firms, or academia.
Environmental Engineering: Environmental engineers focus on designing and implementing solutions to address environmental problems. They work on projects related to water and wastewater treatment, air pollution control, waste management, and environmental impact assessments. They may be involved in the planning, design, construction, and operation of environmental systems. Environmental engineers typically work in engineering firms, government agencies, consulting companies, or industries.
Skillset
Environmental Science: Environmental scientists possess a strong scientific background and research skills. They have knowledge of various scientific disciplines such as biology, chemistry, ecology, and geology. They are skilled in data collection, analysis, and interpretation, and are proficient in environmental monitoring techniques and research methodologies.
Environmental Engineering: Environmental engineers have a solid foundation in engineering principles and design. They possess technical skills related to water and wastewater treatment, air pollution control, waste management, and environmental modeling. They are proficient in using engineering software, conducting feasibility studies, and applying engineering principles to solve environmental problems.
Integration
Environmental Science: Environmental Science integrates knowledge from various scientific disciplines to understand the complex interactions in the environment. It draws upon biology, chemistry, ecology, geology, physics, and other fields to study the environment comprehensively.
Environmental Engineering: Environmental Engineering integrates engineering principles and concepts with environmental science to develop practical solutions. It applies engineering techniques and technologies to address specific environmental problems and create sustainable systems.
While Environmental Science and Environmental Engineering have distinct approaches and areas of focus, they often work collaboratively to address environmental challenges. Both disciplines play crucial roles in understanding, managing, and protecting the environment, and their collective efforts contribute to sustainable development and environmental stewardship.
The important formula in Environmental Science and Environmental Engineering.
In both Environmental Science and Environmental Engineering, various formulas and equations are used to analyze and quantify environmental processes and phenomena. Here are some important formulas commonly used in these fields:
Air Pollution
Air Quality Index (AQI) Calculation:
AQI = ((IAQIhigh – IAQIlow) / (BPhigh – BPlow)) * (C – BPlow) + IAQIlow
IAQI: Individual Air Quality Index for a specific pollutant
BP: Breakpoint concentration
C: Concentration of the pollutant
Water Pollution
Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Saturation Concentration:
DOsat = (14.62 × Temperature in Celsius – 60.7) + (0.12 × Altitude in meters)
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD): BOD = DOinitial – DOfinal
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD): COD = (DOinitial – DOfinal) × Dilution Factor × K
K: Constant related to the specific compound being measured
Water Treatment
Coagulant Dosage:
Coagulant Dosage = (Mf × Vf × C) / (Ms × Vs)
Mf: Molecular weight of the flocculant
Vf: Volume of the flocculant solution
C: Concentration of the flocculant
Ms: Molecular weight of the solid being flocculated.
Vs: Volume of the solid suspension
Solid Waste Management
Waste Generation Rate:
Waste Generation Rate = (Waste Produced) / (Time)
Waste Diversion Rate:
Waste Diversion Rate = (Waste Diverted from Landfill) / (Total Waste Generated)
Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental Impact Score:
EIS = (Importance × Magnitude) / (Control × Reversibility)
Importance: Importance of the impact on a scale of 1-10
Magnitude: Magnitude of the impact on a scale of 1-10
Control: Control measures in place on a scale of 1-10
Reversibility: Reversibility of the impact on a scale of 1-10
Climate Change
Carbon Footprint Calculation:
Carbon Footprint = (Energy Consumption) × (Carbon Emission Factor)
Energy Consumption:
Total energy used in a process or activity
Carbon Emission Factor:
CO2 emissions associated with the energy source
Noise Pollution
Sound Pressure Level (SPL):
SPL = 20 * log10(P / P0)
P: Sound pressure at the measurement location
P0: Reference sound pressure (typically 20 µPa)
These formulas represent just a small subset of the many equations and formulas used in Environmental Science and Environmental Engineering. The specific formulas used can vary depending on the area of study and the environmental parameters being measured or modeled. It is important to consult appropriate references and literature for the specific formulas relevant to your area of interest.
Important question and answer
Certainly! Here are some important short questions and answers related to environmental science and engineering, that might be useful for exams.
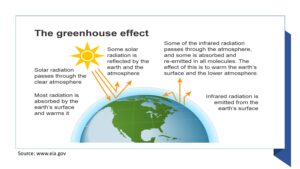
Question: What is the greenhouse effect?
Answer: The greenhouse effect refers to the trapping of heat in the Earth’s atmosphere by greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, leading to global warming.
Question: What is the ozone layer?
Answer: The ozone layer is a region in the Earth’s stratosphere that contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) molecules, which help to absorb and block harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
Question: What is the pH scale used to measure?
Answer: The pH scale is used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a substance. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, values below 7 indicating acidity, and values above 7 indicating alkalinity.
Question: What is biodiversity?
Answer: Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Question: What is eutrophication?
Answer: Eutrophication is the process of excessive nutrient enrichment in a body of water, leading to the overgrowth of algae and other aquatic plants. This can result in oxygen depletion and harm aquatic life.
Question: What is the concept of sustainable development?
Answer: Sustainable development refers to the approach of meeting the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs while considering social, economic, and environmental factors.
Question: What is solid waste management?
Answer: Solid waste management involves the collection, transportation, disposal, and recycling of solid waste materials in an environmentally sound and sustainable manner.
Question: What is renewable energy?
Answer: Renewable energy is energy derived from sources that are naturally replenished, such as solar power, wind power, hydropower, and geothermal energy.
Question: What is the role of environmental impact assessment (EIA)?
Answer: Environmental impact assessment is a process that evaluates the potential environmental effects of proposed projects or activities and helps in making informed decisions to minimize or mitigate these impacts.
Question: What are the major causes of deforestation?
Answer: The major causes of deforestation include logging, agricultural expansion, urbanization, and infrastructure development.
Question: What is the importance of wetlands?
Answer: Wetlands play a crucial role in flood control, water purification, wildlife habitat, and carbon sequestration. They act as natural filters and provide numerous ecological services.
Question: What is the significance of environmental monitoring?
Answer: Environmental monitoring involves the systematic collection and analysis of data to assess the quality of the environment, identify potential risks, and guide decision-making for environmental management and protection.
Question: What are the effects of air pollution on human health?
Answer: Air pollution can cause respiratory problems, allergies, cardiovascular diseases, and other adverse health effects in humans, particularly in vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing conditions.
Question: What is the concept of sustainable water management?
Answer: Sustainable water management involves the efficient use of water resources, conservation measures, water recycling, and the protection of water quality to ensure long-term availability and accessibility of clean water.
Question: What is environmental legislation?
Answer: Environmental legislation comprises laws, regulations, and policies enacted by governments to protect the environment, conserve natural resources, and regulate human activities that may impact the environment.
Question: What are the major sources of water pollution?
Answer: The major sources of water pollution include industrial discharges, agricultural runoff, improper waste disposal, sewage and wastewater discharge, and oil spills.
Question: What is the role of environmental education?
Answer: Environmental education aims to raise awareness, promote knowledge, and foster attitudes and behaviors that contribute to environmental conservation, sustainability, and responsible stewardship of natural resources.
Question: What is the concept of carbon footprint?
Answer: Carbon footprint refers to the total amount of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, emitted directly or indirectly by an individual, organization, or product throughout its lifecycle. It is a measure of their impact on climate change.

Question: What is the concept of waste hierarchy?
Answer: The waste hierarchy is a concept that prioritizes waste management strategies in order of environmental preference: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, and Disposal. It emphasizes the importance of waste reduction and resource recovery.
Question: What are the effects of climate change on ecosystems?
Answer: Climate change can lead to shifts in ecosystems, loss of biodiversity, changes in species distribution, disruption of ecological processes, and increased vulnerability of ecosystems to natural disasters.
Question: What is the concept of environmental justice?
Answer: Environmental justice is the fair and equitable distribution of environmental benefits and burdens among different communities, regardless of their socioeconomic status, race, or ethnicity.
Question: What are the main sources of indoor air pollution?
Answer: Indoor air pollution can be caused by factors such as combustion appliances, tobacco smoke, building materials, household cleaning products, and inadequate ventilation.
Question: What is the concept of sustainable agriculture?
Answer: Sustainable agriculture promotes farming practices that are environmentally friendly, economically viable, and socially responsible, aiming to meet present and future food needs without depleting natural resources or harming the environment.
Question: What are the effects of plastic pollution on marine life?
Answer: Plastic pollution in the oceans can harm marine life through ingestion, entanglement, and habitat destruction. It poses a significant threat to marine ecosystems and biodiversity.
Question: What is the concept of eco-efficiency?
Answer: Eco-efficiency aims to maximize resource productivity and minimize environmental impacts by optimizing the use of resources and reducing waste and pollution in the production and consumption processes.
Question: What is the role of environmental ethics?
Answer: Environmental ethics is the study of ethical principles and values that guide human behavior towards the environment. It promotes a moral responsibility and respect for nature and the well-being of future generations.
Question: What are the impacts of water scarcity?
Answer: Water scarcity can lead to reduced access to clean drinking water, compromised sanitation and hygiene, agricultural productivity losses, conflicts over water resources, and economic challenges in water-dependent industries.
Question: What is the concept of circular economy?
Answer: A circular economy is an economic system that aims to minimize waste and resource consumption by promoting the reuse, recycling, and regeneration of materials and products.
Question: What are the challenges associated with sustainable waste management?
Answer: Challenges of sustainable waste management include implementing effective waste segregation and recycling systems, promoting behavioral change, managing hazardous wastes, and addressing the issue of landfill space.
Question: How does noise pollution impact human health?
Answer: Noise pollution can cause hearing loss, sleep disturbances, stress, impaired communication, and adverse effects on mental and physical health.
Question: What are the causes of soil degradation?
Answer: Soil degradation can be caused by factors such as erosion, deforestation, improper agricultural practices, pollution, and urbanization.
Question: What is the concept of environmental remediation?
Answer: Environmental remediation involves the cleanup and restoration of contaminated sites to mitigate the impacts of pollution and restore the environmental quality.
Question: What is the concept of life cycle assessment (LCA)?
Answer: Life cycle assessment is a systematic analysis of the environmental impacts of a product, process, or activity throughout its entire life cycle, from raw material extraction to disposal.
Question: What are the impacts of deforestation on climate change?
Answer: Deforestation contributes to climate change by reducing the carbon sink capacity of forests, releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, disrupting local weather patterns, and reducing biodiversity.
Question: What is the concept of ecological footprint?
Answer: Ecological footprint measures the amount of land and resources required to sustain an individual, community, or country’s lifestyle and consumption patterns. It helps assess the sustainability of human activities.
Question: What are the environmental impacts of fossil fuel combustion?
Answer: Fossil fuel combustion releases greenhouse gases, particulate matter, and air pollutants, contributing to climate change, air pollution, and respiratory health problems.
Question: What is the concept of environmental risk assessment?
Answer: Environmental risk assessment evaluates the potential risks and hazards associated with specific activities, substances, or projects, helping to identify and implement measures to minimize or mitigate those risks.
Question: What is the role of renewable energy in mitigating climate change?
Answer: Renewable energy sources, such as solar power and wind power, produce lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, making them important in reducing carbon footprint and combating climate change.
Question: What is the concept of environmental monitoring networks?
Answer: Environmental monitoring networks consist of sensors, instruments, and data collection systems deployed in various locations to gather information on air quality, water quality, weather conditions, and ecological parameters.
Question: What are the effects of water pollution on aquatic ecosystems?
Answer: Water pollution can lead to the loss of biodiversity, degradation of aquatic habitats, algal blooms, oxygen depletion, and the decline of fish populations.
Question: How does urbanization impact the environment?
Answer: Urbanization can lead to habitat loss, increased energy consumption, air and water pollution, waste generation, and the fragmentation of natural landscapes.
Question: What is the role of environmental treaties and agreements?
Answer: Environmental treaties and agreements establish international frameworks and commitments to address global environmental challenges, such as climate change, biodiversity conservation, and pollution control.
Question: What are the impacts of climate change on agriculture?
Answer: Climate change can affect agricultural productivity through changes in temperature, precipitation patterns, and the incidence of pests and diseases, posing risks to food security and rural livelihoods.
Question: What is the concept of sustainable transportation?
Answer: Sustainable transportation aims to reduce the environmental impacts of transportation systems by promoting the use of public transportation, cycling, walking, and electric vehicles, and improving fuel efficiency.
Question: What are the environmental impacts of mining activities?
Answer: Mining activities can result in deforestation, soil erosion, water pollution, habitat destruction, and the release of toxic substances into the environment.
Question: What is the concept of green building design?
Answer: Green building design focuses on creating energy-efficient, environmentally friendly, and sustainable buildings by incorporating features such as renewable energy systems, efficient insulation, and water conservation measures.
Question: What are the effects of ocean acidification?
Answer: Ocean acidification, caused by increased carbon dioxide absorption by the oceans, can harm marine organisms, including coral reefs, shellfish, and other marine life that rely on calcium carbonate structures.
Question: What is the concept of environmental stewardship?
Answer: Environmental stewardship refers to the responsible and sustainable management and conservation of natural resources, with a focus on long-term sustainability and the well-being of ecosystems and future generations.
Question: How does waste-to-energy conversion work?
Answer: Waste-to-energy conversion involves the conversion of waste materials, such as municipal solid waste or biomass, into energy through processes such as incineration or anaerobic digestion, helping to reduce waste volume and generate electricity or heat.
————–********————–
Must read
- Chemical Engineering || Introduction || Carrier 2023
- Introduction to Heat transfer || Chemical Engineering
- Mass Transfer || Chemical Engineering
- Introduction to Chemical Reaction Engineering
- Basics of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
- Fluid Flow Operation aka Fluid Mechanics
————–*******—————

