The production of clean, sustainable, and profitable hydrogen production processes is crucial for the commercial success of hydrogen vehicles or hydrogen-related research activities. The hydrogen production roadmap explores three basic and promising technological possibilities for hydrogen production. This article will be focusing on three key hydrogen production technologies.
Table of Contents
What is hydrogen?
Hydrogen is the cleanest fuel we have ever seen. Hydrogen is produced naturally from water and is abundant in nature. However, we need to find ways to produce it efficiently and safely. Hydrogen is a chemical element that occurs naturally in small amounts in many substances. Hydrogen is the simplest atom in the universe, consisting of only one proton (positively charged particle) and one electron (negatively charged). In its purest state, hydrogen gas consists entirely of protons and electrons; however, due to the extremely low mass of these particles, they rarely exist independently.
Click here to read about 35 interesting facts about hydrogen
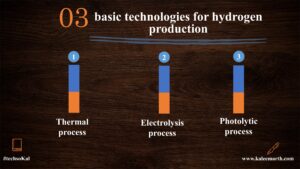
3 basic technologies for hydrogen production
There are three different processes of hydrogen production as below:
- Thermal process
- Electrolysis process
- Photolytic process
Each processing method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Let’s take a look at each of these methods with their pros and cons.
i. Thermal process:
In this process, the stored energy resources such as coal or biomass is being used to produce hydrogen in their molecular structures. Another type uses heat in combination with closed chemical cycles to produce hydrogen from raw materials, such as water; these are known as “thermochemical” processes. The thermal process could be categorized as below:
- Distributed Natural Gas Reforming
- Bio-Derived Liquids Reforming
- Coal and Biomass Gasification
- Thermochemical Production (Using a heat-induced chemical reaction to split water)
Pros:
- Lowest current cost
- Existing feedstock infrastructure
- The most feasible approach to building a short-term hydrogen market
Cons:
- Requires high voltages
- High capital costs
- High operation costs
- High maintenance costs
- Design for manufacturing
- Not environmentally friendly
ii. Electrolytic process:
This is the oldest way of producing hydrogen. It involves splitting water into oxygen and hydrogen using electricity. In order to do this, you need two electrodes, one positive and one negative. You then connect them to a power supply and apply a voltage between them. When you do this, electrons flow from the positive electrode to the negative electrode. These electrons cause the water molecules to split apart and release their hydrogen atoms.
Pros:
- Simple process
- Cheap
- Easy to use
Cons:
- High capital costs
- Low system efficiency
- Requires high voltages
- Not environmentally friendly
iii. Photolytic process:
The photolytic process is the decomposition of water molecules by sunlight. In this process, the water molecule breaks down into oxygen and hydrogen gas. This reaction occurs naturally in the atmosphere but can be accelerated by artificial means. Photolytic processes use the energy of light to divide the water and converted it to hydrogen and oxygen. These processes are currently in the very early stages of research and offer the long-term potential for sustainable hydrogen production with low environmental impact.
Pros:
- Simple process
- It can operate at low temperatures
- Easy to use
- Environmentally friendly
- Clean and sustainable
- Using only water and solar energy
Cons:
- Low system efficiency
- A cost-effective reactor is required
- Effective photocatalyst material is under development
Conclusive remarks:
Although each hydrogen production and generation technologies face specific technical challenges, there are common hurdles for most technology options. Development and demonstration activities to address these challenges are still required to pave the way for successful commercialization and widespread use of hydrogen as an energy carrier.
Read more articles:

6 thoughts on “3 basic technologies for hydrogen production: an overview”